Update… Created back in May of 2021 (…a world ago, in internet terms; a world ago, in terms of the present moment…), I’ve edited this post to include images of the matzevot (tombstones) of Jack Bartman, and his parents, Morris and Gussie, which appeared on FindAGrave in 2023 and 2021, respectively.
The post also includes the full text of an article from issue 29 of the publication “der Vinschger”, entitled “Als in Göflan der Bomber „landete”” (“When the Bomber “Landed” in Göflan“), published in the town of Schlanders (and available at https://www.dervinschger.it/de/) in September of 2020, which includes an image of the wreckage of B-17G 44-6861. I’ve included the article’s original German text and an English-language translation, the latter appearing in dark blue, like this.
The story of the crew’s final flight in 44-6861, as highlighted in the “Als in Göflan der Bomber „landete”” (“When the Bomber “Landed” in Göflan”) specifically mentions the names of three of the bomber’s ten crewmen: pilot 1 Lt. Eugene T. Bissinger, navigator 1 Lt. Manton A. Nations, and, Cpl. Bartman himself. Therein, Jack Bartman’s fate is recounted in one sentence: “Einer der abgesprungenen Soldaten, Jack Bartman, wurde von fanatischen Widerstandskämpfern erschossen.” (“One of the soldiers who jumped [from the] ship, Jack Bartman, was shot by fanatical resistance fighters.”)
There’s no mention that Cpl. Bartman was murdered because he was a Jew.
Likewise, NARA RG 153 War Crimes Case File 16-293-16 specifically states that one or more of the men involved in Cpl. Bartman’s murder – Giovanni (Johann) Weiss, Kurt Gerlitsky (Gerlitzki), and Gottfried Marzoner – were members of the “Landwacht” (Land Watch? Land Guard?), which – putting it mildly – would’ve been the utter antithesis of any Resistance movement. Likewise, the Burgomeister of Lauregno also participated in Cpl. Bartman’s murder.
Otherwise, Ancestry.com reveals that T/Sgt. Francis Xavier Kelly (son of John F. (or Joseph J.?) and Elizabeth (Gaffney) Kelly) – whose report in MACR 13817 is so instrumental in reconstructing the events surrounding Cpl. Bartman’s fate – was born in Brooklyn on December 2, 1924, and passed away at the age of seventy years on June 13, 1994.
And so, here’s the revised post…
______________________________
“IT’S EASY TO REALIZE THE ANGUISH THE BOY’S FAMILY MUST BE ENDURING AS A RESULT OF NOT RECEIVING A PROPER STORY OF WHAT HAPPENED TO THEIR SON.
IT’S ALSO NICE TO KNOW THAT SOMEONE IS DEFINITELY INTERESTED IN HELPING THEM BY A THOROUGH INVESTIGATION OF THE CASE.
IN THAT RESPECT, I HOPE THIS INFORMATION WILL BE OF VERY GREAT VALUE TO YOU.
IN FACT, I AM WILLING TO HAVE YOU CALL ON ME AT ANY TIME FOR ANYTHING I MAY HAVE MISSED, FOR I AM VERY EAGER TO BE OF ASSISTANCE.”
– Francis X. Kelly, March 4, 1946
____________________
Corporal Jack Bartman
Saturday, September 6, 1924 – Friday, April 20, 1945
– .ת. נ. צ. ב. ה –

“וְגִלְּתָ֚ה הָאָ֙רֶץ֙ אֶת־דָּמֶ֔יהָ וְלֹֽא־תְכַסֶּ֥ה ע֖וֹד עַל־הֲרוּגֶֽיהָ…”
“…and the land shall reveal its blood and it shall no longer conceal its slain ones.” (Isaiah 26:12)
________________________________________
My recent post – focusing on Captain Paul Kamen, PFC Donald R. Lindheim, and PFC Arthur N. Sloan of the United States Army, as well other Jewish military casualties that occurred less than three weeks before the Second World War’s end – is incomplete, for it lacks a name and story which follows below: That of Corporal Jack Bartman of the United States Army Air Force.
An aerial gunner in the Italy-based 15th Air Force, he was captured – unwounded; uninjured – but never experienced the end of the war in Europe eighteen days later, let alone an eventual return to his family: He was murdered by civilians very shortly after being taken captive. Possibly because, much as could befall most any soldier or aviator – he was captured at the very wrong place; at the very wrong time. Equally – to an extent that will never be fully known, but whether an extent lesser or greater (and probably much greater) – because he was a Jew. In a larger sense, his story relates to the predicament of captured Jewish soldiers and airmen in the European Theater during WW II, albeit this varied enormously between Jewish soldiers captured while serving in the armed forces of the United States and British Commonwealth, versus those serving in the armed forces of Poland and the Soviet Union.
As such, Cpl. Bartman’s murder at the hands of civilians, and the disillusioning postwar outcome (well, there was no real outcome as such) of the postwar investigation into his murder thus merits “this” separate blog post.
____________________
Jack Bartman (32883370), the son of Morris and Gussie (Needleman) Bortnicker, and the brother of Simon, was born in Manhattan on September 6, 1924, his family eventually residing at 487 Snediker Ave, in Brooklyn. Originally assigned to the 8th Air Force, he was, “One of hundreds of surplus 8th Air Force gunners who sailed from Glasgow, Scotland, docking at Naples, Italy, for assignment with the 15th Air Force.” Assigned to the 840th Bomb Squadron of the 483rd Bomb Group, he had no aircrew of his own, filling-in with crews as needed for combat missions.
____________________
Jack Bartman

Jack Bartman’s Draft Registration Card

This image shows Jack Bartman and his (original?) crew during training at Ardmore, Oklahoma, in July of 1944. Jack is is the first row, second from right. The names of the other men are unknown, albeit the four in the rear (as seen in so many similar photos from the war) would have been the pilot, co-pilot, navigator, and bombardier, while the five men in the front row with Jack would have been the flight engineer, radio operator, and other aerial gunners. On the reverse of the image is the notation “Fonville Studio, Ardmore Oklahoma, July 21, 1944.”
 Assigned to the crew of 1 Lt. Eugene T. Bissinger on April 20, 1945, his “un-nicknamed” B-17G Flying Fortress, serial number 44-6861, was shot down during a mission to marshalling yards at Fortezza, Italy (the same target which claimed the crew of 2 Lt. Earle L. Sullivan of the 342nd Bomb Squadron of the 97th Bomb Group, among whom was tail gunner S/Sgt. David Weinstein), his plane’s loss being covered in Missing Air Crew Report (MACR) 13817.
Assigned to the crew of 1 Lt. Eugene T. Bissinger on April 20, 1945, his “un-nicknamed” B-17G Flying Fortress, serial number 44-6861, was shot down during a mission to marshalling yards at Fortezza, Italy (the same target which claimed the crew of 2 Lt. Earle L. Sullivan of the 342nd Bomb Squadron of the 97th Bomb Group, among whom was tail gunner S/Sgt. David Weinstein), his plane’s loss being covered in Missing Air Crew Report (MACR) 13817.
The bomber’s crew that day comprised:
1 Lt. Eugene T. Bissinger – Pilot – Prisoner of War at Merano, Italy
2 Lt. Donald W. McGinnis – Co-Pilot – Evaded capture (originally in Parrish crew)
1 Lt. Manton A. Nations – Navigator – Prisoner of War at Merano, Italy (original crew member of Jack Bissinger)
S/Sgt. Lee Hugh Shead – Togglier (enlisted bombardier) – Prisoner of War at Merano, Italy (originally in Urschel crew)
T/Sgt. Willie D. McDaniel – Flight Engineer – Evaded (originally in Urschel crew)
T/Sgt. Francis X. Kelly – Radio Operator – Evaded (originally in Urschel crew)
S/Sgt. Edmund T. Farrell – Gunner (Right Waist) – Evaded (originally in Urschel crew)
S/Sgt. Marvin I. Mattatall – Gunner (Ball Turret) – Evaded (originally in Alford crew)
S/Sgt. Peter A. Filosema – Gunner (Tail Gunner) – Evaded (originally in Urschel crew)
____________________
As shown from the above list, interestingly, Eugene Bissinger’s crew for the April 20 mission was a composite crew, his only “original” crew member – assigned during training at MacDill Field, Florida – having been Manton Nations. Donald McGinnis was a member of the Thomas E. Parrish crew. Willie McDaniel, Lee Shead, Francis Kelly, Edmund Farrell, and Peter Filosema had been crew members of George C. Urschel, Jr., while Marvin Mattatal was a member of the William Alford crew.
The below photo, of George C. Urschel’s crew, includes five men who served in Jack Bissinger’s crew on April 20. The men are, left to right:
Rear row:
Raymond J. Kosinski – Bombardier (Urschel crew) – POW 4/20/45
Ira Geifer – Co-Pilot (Urschel crew)
George C. Urschel – completed missions
Carl R. Helfenberger – Navigator (Urschel crew) – completed missions
Front row:
Willie D. McDaniel
Francis X. Kelly
Anastasios T. Cokenias – Waist Gunner (Urschel crew) – Completed missions
Peter A. Filosema
Edmund T. Farrell
Lee H. Shead

The loss of B-17G 44-6861 is covered in MACR 13817, the first page of which is shown below…

____________________
What happened to Jack Bartman? Well, rather than simply display a bunch of images without comment or explanation, what follows is an account based upon information from Casualty Questionnaires in MACR 13817 (by Bissinger, Kelly, Mattatall, McDaniel, Nations, and Shead) and, Case File 16-293-16, the latter from NARA Records Group 153 (Records of the Judge Advocate General of the United States Army). The latter document covers the investigation into Jack Bartman’s murder, and includes the names of both accused and witnesses, which can be found below.
____________________
And so…
Shortly after noon on April 20, 1945, as the 483rd’s formation rallied off Fortezza for return to its base at Sterparone, Italy, aircraft 44-6861 was struck by flak behind its #1 or #2 engines while flying at an altitude of 27,000 feet. Some witnesses reported that fuel began to spray from its damaged left wing, while others described flames flaring from under the #1 engine’s supercharger, with smoke – turning from gray to black – trailing behind.
Remarkably, this event was photographed from the radio room or dorsal turret of a nearby B-17, the resulting image becoming Army Air Force photo 60096AC / A22790. The photo clearly shows Lt. Bissinger’s 44-6861 trailing smoke or fuel from behind its #1 engine. Close examination of the picture reveals the tail insignia of the damaged plane to be a white “Y” upon a black background, with a lack of any geometric and / or numerical markings beneath the aircraft’s serial number: The markings of the 483rd Bomb Group.

Caption: “During the raid on the marshalling yards at Fortezza, Italy on April 20, 1945 this Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress of the 15th A.F. was hit by flak and caught fire. One of the greatest flak gun concentrations was massed in northern Italy before the Germans were beaten back to the Po River.”
________________________________________
The bomber, fortunately not actually aflame, then dropped back from the 840th Bomb Squadron’s formation. With the plane skidding and quickly losing altitude, though remaining in level flight, five crewmen parachuted almost immediately, and a further two jumped soon after, all these crewmen exiting the bomber at a location ten to twenty-five miles due west of Fortezza, or, between Fortezza and a point 20 miles southwest of Merano.
The aircraft was last seen by other members of the 840th Bomb Squadron just south of the town of Stelvia, losing altitude over the Alps in a direction northwest from Fortezza, and then going out of sight in the haze, possibly at an altitude of eight to ten thousand feet.
________________________________________
Here’s a map of the last reported location of 44-6861, from MACR 13817: Near Stelvio, Italy.
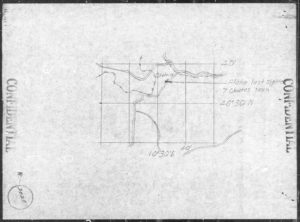
By way of comparison, here’s an Oogle Map photo (air or satellite? – I’m not sure which) of the area in the above map, very roughly at the same scale as the map itself, with Stelvio in the center of the image. While not apparent from the map, immediately obvious from the image is the mountainous nature of the terrain.

________________________________________
Digressing… To give you a better idea of the appearance of 483rd Bomb Group B-17s (the 15th Air Force, let alone other numbered Air Forces of the WW II Army Air Force, having received markedly less attention over the decades following WW II than the 8th Air Force, but that’s getting off-topic…) here are a photo and painting of two different 483rd Bomb Group B-17s.
First, the photo: “Heading for its target, the Vienna Schwechat Oil Refineries in Austria, are bombs from one of the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortresses of the 15th AF that attacked this one of the few remaining sources of oil left to the Hun in Europe, on 7 Feb. 1945”.
The “un-nicknamed” B-17G in this image (Army Air Force Force photo 61599AC / A4991) – aircraft 44-6325, of the 816th Bomb Squadron – would be lost a little over a month later, on March 16, 1945, during a mission to that same target, though no cause of the plane’s loss is given in MACR 13059, which covers the incident. Piloted by 1 Lt. Homer R. Anderson, the plane crash-landed behind Soviet lines southeast of Lake Balaton, Hungary, with all ten crewmen aboard. The entire crew – all uninjured in the incident – eventually returned to the United States.
The image provides an excellent illustration of the relatively plain appearance of 15th Air Force (5th Bomb Wing, to be specific) B-17s, which bore far simpler, far less colorful unit insignia than Flying Fortresses of the 8th Air Force. Typical of 483rd Bomb Group planes, this aircraft bears a simple star beneath the “Y” symbol carried by all 5th Bomb Wing (15th Air Force) B-17s, and – like other planes of the 483rd Bomb Group – lacks any form of squadron identification.

________________________________________
Second, the painting: Here is B-17G 44-6538 “Miss Prissy” of the 817th Bomb Squadron, as depicted by Don Greer in B-17 Flying Fortress in Color (1982). The image provides an illustration of the red rudders and cowl rings of 483rd Bomb Group B-17s, not evident from the black and white photos above.
This aircraft, piloted by 1 Lt. Ralph F. Bates, failed to return from a mission to oil refineries at Ruhland, Germany, on March 22, 1945. Subsequent to an attack by German fighters after bombs-away – which caused the bomber’s right main fuel tank to catch fire – five enlisted personnel (Brennan J., McCauley, Pickard, Piersall, and Thaen) bailed out, to be captured and interned at Stalag Luft I, while the flight engineer (Brewer) remained aboard with the plane’s four officers (Bates, Kallock, Fischer, and Jacobs). The aircraft eventually landing somewhere behind Russian lines. Fortunately, all of MISS PRISSY’S ten crew members eventually returned to the United States. The plane’s loss is covered in MACR 13242.

________________________________________
Here’s the insignia of the 840th Bombardment Squadron, from the American Air Museum in Britain.

________________________________________
Back to the story…
This was the last that was known of the plane and crew until not long after the war’s end.
It turned out that eight crewmen – not seven – parachuted from the plane, with Lieutenants Bissinger and Nations (the latter in the co-pilot’s seat) remaining in the aircraft. The two then crash-landed the plane – probably because the plane had descended too low to safely bail out? – with the bomber’s crew members giving different accounts of where it finally came to earth: According to Lt. Bissinger, “in a valley of a mountain 50 to 75 miles S.W. by W. of Fortezza”; according to Lt. Nations, “about 20 miles S.W. of Merano”; according to T/Sgt. McDaniel, “10 miles from Switzerland”; according to S/Sgt. Mattatall, (not a regular member of the Bissinger crew) “20 miles from Fondo Italy.”
Both men suffered cuts and severe bruises in the landing (and Bissinger a broken left hand) but they were uninjured by flak.
According to an entry by Manfred Haringer at https://b17flyingfortress.de/, Bissinger and Nations actually crash-landed 44-6861 in the vicinity of the village of Göflan (otherwise known as Covelano or Goldrain), near the town of Schlanders (otherwise known as Silandro) in the Adige river valley, in the South Tyrol.
Captured, these two officers remained in a German hospital in Merano until the war’s end. According to Lt. Nations, also at the hospital were “T/Sgt. Kolbe” and “S/Sgt. Mountain” and a second (un-named) Staff Sergeant, the latter I think togglier S/Sgt. Shead. As for “Kolbe” and “Mountain”, strangely, these names don’t correspond to any American POWs in the European Theater, whether from Army ground forces or Army Air Forces.
The other casualty in the crew was flight engineer McDaniel, who, hit by flak in the shoulder, arm, and cheek, and an evader, was given medical treatment by “a German woman doctor through Partisan activities”.
Six other crew members were more fortunate. According to radio operator Kelly, co-pilot McGinnis, McDaniel, and three aerial gunners (right waist gunner Farrell, ball turret gunner Mattatall, and tail gunner Filosena), evaded capture, probably remaining hidden in the area between Merano, and Göflan, and Schlanders.
____________________
As for Corporal Jack Bartman? Taken as a whole, the Casualty Questionnaires of his fellow crewmen recount the same appalling event, with Francis Kelly’s account being by far the most detailed.
Eugene Bissinger: “Jack Bartman was brutally beaten by Italian civilians and finally shot by one of them. The name of the town and the man who did the shooting can be found in the statement of a 2nd Lt. Robert G. Henry 02058804 submitted to Escape Section, of Headquarters Fifteenth Air Force, Bari Italy.”
(2 Lt. Robery G. Henry of Paris, Texas, was the co-pilot of Queen Anne / 53, a B-24H Liberator (42-95458 – see MACR 10937) of the 722nd Bomb Squadron, 450th Bomb Group, piloted by 1 Lt. Louis M. McCumsey, shot down during a mission to the Brenner Pass on December 29, 1944. Coincidentally, his plane crashed near Laurein (Lauregno). Nine of his plane’s ten crewmen survived. Having been an evader, Lt. Henry’s name doesn’t show up in Luftgaukommando Report KSU / ME 2651, which has “gaps” in the data fields where the co-pilot’s and navigator’s (Lt. Halstead) names would appear. Thus, it would seem that navigator Lt. Halstead also evaded capture.)
Manton Nations: “Believe to have parachuted safely to ground. Taken by Italian civilians as prisoner. His fate was due to their actions.” Source of information? “Lt Henry of Texas (Paris Texas) B-24 pilot who spent 6 or 7 mo. with Italian Partisans. He saw our plane go down.”
Marvin Mattatall: “I saw him when he bailed out. He was standing by the waist hatch.” “He was killed by German civilians. A civilian by the name of Wisse shot him after being badly beaten by them.” “The information given below was told to me by several Italian civilians. A full account of the incident was given by me and others of the crew to an intelligent [sic] officer at Bolzano and 15th A.A.F.H.Q. in Italy.”
Willie McDaniel: “”Any explanation of his fate based in part or wholly on supposition: “Only because he was of Jewish nationality.””
Lee Shead: “…he was captured and beat to death by civilian personel.” “I saw in the prison camp where I was held a few of his personal belongings and dog-tags. There was also a report stating that he was killed while resisting arrest. There was also a map showing his burial place.”
Due to the detail and comprehensiveness of Kelly’s account, I’ve included images and transcripts of his Casualty Questionnaire, which you can read below.
Kelly’s report can be summarized as follows:
Like the seven other crewmen who parachuted from 44-6861, Corporal Bartman landed without injury. This was near the town of Lauregno (more commonly and better known today as Laurein?).
“Laurein am Deutschnonsberg in Südtirol“: Laurein (Lauregno), Italy, in late 2012

An Oogle Air photo of Laurein (Lauregno).

This Oogle map of the South Tyrol shows the relative locations of Göflan (Covelano / Goldrain), Laurien (Lauregno), and Merano. Note Bolzano to the southeast.

Upon landing, Cpl. Bartman was first encountered by a friendly civilian (name unknown) who intended to help him evade capture. But, uncertain of the situation, Bartman hesitated, and tragically, the opportunity for evasion was immediately lost: He was captured other civilians, who were led by the Burgomeister and among whom was a certain Giovanni (Johann) Weiss.
Bartman was disarmed (presumably of his .45 pistol?), and then, he was beaten.
He was ostensibly to have been taken to the prisoner of war camp at Merano, though – in light of the near-48 kilometer (nearly 30 miles) distance between that town and Lauregno – Kelly does not specify if this was to have been via motor vehicle or (?!) on foot.
According to Oogle Maps, Merano and Laurein are today connected by roads SP86 and SS238, as shown in the map below.
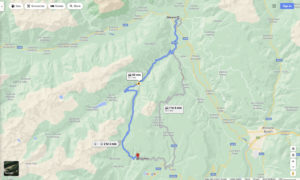
Assuming that there was ever any real intention about his internment at Merano, the point soon became horribly moot. En route, civilians beat Corporal Bartman once again. Then, he was shot in both legs. Unable to continue walking, he was then murdered.
____________________
Four days later, he buried in the city cemetery of Merano with neither a coffin nor identification. The location of his intentionally un-named grave was marked by Italian civilians sympathetic to the Allies, reportedly among them the civilian who first encountered and attempted to aid the Corporal. This man led American authorities to the grave after the war’s end, and Cpl. Bartman’s body was reinterred at the United States Military Cemetery at Mirandola in early June. More about this can be found in the letter – below – by Arini Adelino of Merano (the letter was incorporated into Corporal Bartman’s Individual Deceased Personnel File – IDPF), to the Allied Military Government.

To the
Allied Military Government
Merano
Through this I inform you, that on April 24th 1945, 9 o’clock in the morning, the corpse of the American pilot, Jack Bartman, who was killed by a member of the country guard (“Landwacht”) near the Palade Pass, was buried in the city cemetery by order of the German military commando (Platzkommando).
By order of the German political commissioner, Franz Huber, the American soldier was not buried in the heroes cemetery (Heldenfriedhof), but was buried without honors in a simple hole without a casket in the corner of the dishonorable (murders and suicides).
I protested against this and told the political commissioner, that such a treatment was inhuman and unjust, but I could not attain anything, because Mr. Huber said, that the corpse did not deserve anything better, as he defended himself against the him [sic] arresting country guard (Landwacht) and as he was a Jew.
Il. Direttore del Cimitero
Arini Adelino
____________________
Sgt. Kelly received this information while in hiding at two towns – one German, and another Italian – and noted that these reports coincided with stories given to the other evadees in his crew.
Kelly’s civilian informants included:
In Marcena di Rumo (presumably, the Italian town):
An “unknown eyewitness”
Elena Torresani
In Proveis (the German town):
Johann Pichler
In the Italian towns of, Brez, Fondo, and Marcena di Lanza
Unidentified civilians
____________________
Here are images and transcripts of Sergeant Francis X. Kelly’s Casualty Questionnaire, Individual Casualty Questionnaire, and additional correspondence, from MACR 13817.

Casualty Questionnaire
Your name:
FRANCIS X. KELLY
Rank:
T/SGT.
Did other members of crew bail out?
YES, ALL EXCEPT THE NAVIGATOR AND PILOT BAILED OUT IMMEDIATELY
Tell all you know about when, where, how each person in your aircraft for whom no individual questionnaire is attached bailed out. A crew list is attached. Please give facts. If you don’t know, say: “No knowledge”.
CO-PILOT, ENGINEER, 3 GUNNERS, AND MYSELF (RADIO GUNNER) WERE EVADES AFTER BAILING OUT. TOGGLIER BAILED OUT AND WAS TAKEN POW. OTHER GUNNER BAILED OUT SUCCESSFULLY, BUT WAS KILLED BY GERMAN CIVILIANS.
Where did your aircraft strike the ground?
NO KNOWLEDGE
What members of your crew were in the aircraft when it struck the ground? (Should cross check with 8 above and individual questionnaires.)
PILOT AND NAVIGATOR RODE THE SHIP TO THE GROUND
Where were they in aircraft?
IN PILOT’S AND CO-PILOTS POSITIONS
What was their condition?
NAVIGATOR WAS SLIGHTLY INJURED BY FLAK, PILOT WAS OK, BUT BOTH WERE INJURED BY CRASH. (BROKEN ARMS FOR EACH.)
Individual Casualty Questionnaire
Did he bail out?
YES
Where?
ABOUT 10 MILES WEST OF BOLZANO, ITALY
Last contact or conversation just prior to or at time of loss of plane:
AT THE SIDE DOOR OF THE PLANE WHILE PREPARING TO BAIL OUT
Was he injured?
NO
Where was he last seen?
I NEVER SAW HIM AFTER LEAVING PLANE
Any hearsay information:
FROM GERMAN AND ITALIAN NATIVES, I WAS FULLY INFORMED OF HIS DEATH. HE WAS KILLED BY GERMAN CIVILIANS UPON LANDING. I CAN GIVE DEFINITE NAMES AND PLACES AND WILL TYPE THEM ON BACK OF THIS SHEET. THESE PEOPLE CAN GIVE FULL DETAILS. THERE ARE A FEW EYE WITNESS[ES] IN THE TOWNS I WILL MENTION.
Any explanation of his fate based in part or wholly on supposition:
NOT TO MY KNOWLEDGE
Total number of missions of above crew member:
IT WAS HIS 33RD MISSION
Pages three and four – additional correspondence

Page “three”
(WHEN I LEFT THE SECTION, THE MAN NAMED WEISS WAS BEING HELD UNDER ARREST BY ITALIAN PARTISANS IN THE TOWN OF BREZ.)
ACCORDING TO THE INFORMATION I WAS GIVEN, AND WHICH I CHECKED AS BEST I COULD, CPL. BARTMAN HIT THE GROUND NEAR THE TOWN OF LAUREGNO, AND WAS CAPTURED SOON AFTER BY GERMAN CIVILIANS. THE CIVILIANS WERE LED BY THE TOWN BURGOMEISTER, AND A CIVILIAN NAMED WEISS, WHO WERE RESPONSIBLE FOR HIS DEATH. THEY TOOK HIM INTO LAUREGNO AFTER DISARMING AND BEATING HIM. FROM THERE HE WAS TAKEN TO MERANO WHERE THERE WAS A PW CAMP, BUT EN ROUTE, THE CIVILIANS BEAT CPL. BARTMAN SOME MORE, SHOT HIM IN THE BACK OF EACH LEG AND TRIED TO GET HIM TO CONTINUE TO MARCH. AT THIS POINT I UNDERSTAND THAT HE WAS UNABLE TO CONTINUE, SO AFTER ANOTHER BEATING, ONE OF THE CIVILIANS PUT A GUN TO HIS HEAD, AND KILLED HIM. THEN THEY BURIED HIM IN AN UNMARKED GRAVE, BUT SOME ITALIAN SYMPATHIZERS MARKED THE SPOT AND IT SHOULD HAVE BEEN POINTED OUT TO AMERICAN AUTHORITIES WHEN THEY ARRIVED. I LEFT THE SECTION BEFORE THE AMERICANS ARRIVED, SO I DON’T KNOW IF IT EVER WAS BROUGHT TO ANYONE’S ATTENTION.
THE INFORMATION I RECEIVED WAS GIVEN TO ME IN TWO DIFFERENT TOWNS, ONE GERMAN AND THE OTHER ITALIAN, AND INCIDENTALLY COINCIDES WITH THE STORIES GIVEN BY OTHER MEMBERS OF THE CREW WHO WERE HIDING OUT IN OTHER TOWNS.
IN MARCENA DI RUMO, THERE WAS AN EYEWITNESS BUT I DON’T KNOW HIS NAME. THE WOMAN WHO HELPED ME WAS NAMED ELENA TORRESANI, AND SHE WOULD BE ABLE TO GIVE INFORMATION ALONG THOSE LINES. ALSO IN THE TOWN OF PROVEIS (GERMAN), WHERE A MAN NAMED JOHANN PICHLER HELPED ME YOU COULD FIND MORE INFORMATION. I KNOW NATIVES IN THE TOWNS OF BREZ, FONDO, AND MARCENA DI LANZA ARE FULLY AWARE OF THE FACTS SO I SUGGEST THESE PEOPLE BE APPROACHED. INCIDENTALLY ALL THESE TOWNS ARE IN NORTH ITALY, ABOUT 25-30 MILES DIRECTLY WEST OF BOLZANO.
THE KILLING OCCURRED ON APRIL 20, 1945.
Francis X. Kelly
Page “four”
March 4, 1946
295 ST JOHNS PLACE
BROOKLYN, NEW YORK
DEAR SIR,
I HOPE I CAN BE OF SOME ASSISTANCE WITH THE ENCLOSED PARTICULARS. HAVING BEEN ON THE MISSION INVOLVED AND HAVING LIVED IN THE IMMEDIATE VICINITY OF THE SLAYING, I CAN HONESTLY AND DEFINITELY STATE THAT THESE ARE TRUE FACTS I’M PASSING ON, OR AT LEAST AS TRUE AS CAN BE FOUND OUT SO FAR. PERHAPS MORE INFORMATION CAN BE LOCATED BY LOOKING UP THE WAR CRIMES COMMISSION CASE AGAINST A GERMAN CIVILIAN NAMED WEISS, WHO LIVED IN THE TOWN OF LAUREGNO, SOUTH TIROL, NORTH ITALY. HE WAS UNDER ARREST IN THE TOWN OF BREZ, NORTH ITALY, HELD BY ITALIAN PARTISANS, TO BE TRIED FOR THE KILLING OF CPL. BARTMAN.
INTELLIGENCE OFFICERS AT BOLZANO, ITALY, AND AT 15TH AF HDQ., BARI, ITALY, HAVE RECEIVED SWORN STATEMENTS FROM THREE OTHER CREW MEMBERS AS WELL AS FROM MYSELF CONCERNING THE CASE.
IT’S EASY TO REALIZE THE ANGUISH THE BOY’S FAMILY MUST BE ENDURING AS A RESULT OF NOT RECEIVING A PROPER STORY OF WHAT HAPPENED TO THEIR SON. IT’S ALSO NICE TO KNOW THAT SOMEONE IS DEFINITELY INTERESTED IN HELPING THEM BY A THOROUGH INVESTIGATION OF THE CASE. IN THAT RESPECT, I HOPE THIS INFORMATION WILL BE OF VERY GREAT VALUE TO YOU. IN FACT, I AM WILLING TO HAVE YOU CALL ON ME AT ANY TIME FOR ANYTHING I MAY HAVE MISSED, FOR I AM VERY EAGER TO BE OF ASSISTANCE.
I WOULD APPRECIATE A REPLY TO LEARN FOR MYSELF WHAT HAS BEEN DONE IN THE NAME OF JUSTICE, AND AGAIN PLACE MYSELF AT YOUR DISPOSITION.
RESPECTFULLY,
Francis X. Kelly
________________________________________
And there the story continued. That is, at least for a time.
As documented in Case File 16-293-16 of the Judge Advocate General’s Office – documentation for which commenced in mid-June, 1945 – those accused of Jack Bartman’s murder, and witnesses to the event, were identified by May of 1946.
But, by May 3, 1947, the Case was closed.
What happened?
Typical of other War Crimes Case Files, much of Case File 16-293-16 is comprised of both relatively boilerplate-ish correspondence about the status and progress of and about the investigation, and more importantly, information – eyewitnesses reports; interrogation transcripts; depositions – concerning the details of the Case itself. Albeit, the latter information is still nominally present.
As such, three particular documents stand out:
First, a letter of March 4, 1946, written to the Army by Jack’s brother Simon. Note that Simon’s letter was written the same day that Francis Kelly completed his Casualty Questionnaire (above) for the Missing Air Crew Report.
Second, a Docket Sheet listing the names of both accused and witnesses.
Those accused were:
Giovanni (Johann) Weiss
Kurt Gerlitsky (Gerlitzki)
Gottfried Marzoner
Gerlitsky / Gerlitzki and Marzoner were in mid-1946 interned at the “339 PW Camp”, location unspecified. (In Germany?)
The German officer was:
Major Heinemann, accused of refusing Corporal Bartman an honorable burial
Witnesses were:
Adelino Arini
Alois (Luigi) Brugger
Giuseppe Gaiser
Francesco Huber
Luigi Pircher Pancrazi
Federico Segna
…and…
Dr. Veith
Third, the two “final” records in the File, both dated May 3, 1947:
1) A letter by Theater Judge Advocate Colonel Tom H. Barrett (of the Judge Advocate General’s Department) to the Civil Affairs Division of the War Department, indicating that the case was now “administratively closed”, the reasons being presented in the “next” letter, also by Colonel Barrett…
2) …Colonel Barret’s above-mentioned letter, sent to the Deputy Theater Judge Advocate, 7708 War Crimes Group, USFET.
The reasons given for closure of the case?
First, an inability to proceed with further investigation because the accused were by then in Germany, “…most of the accused are either in Germany or in other areas under your jurisdiction [where?] and therefore the investigation cannot be completed in this theater.”
Second, the impending closure of War Crimes investigations by May 1, 1947: “In view of the imminent close-out of this theater and the necessity of terminating the War Crimes investigations on 1 May to permit the completion of cases now ready for trial…”
Third (here, a carefully and diplomatically phrased sense of disillusionment and exasperation emerges from Colonel Barrett’s letter) a reduction in staff to a point that made further investigations of war crimes impracticable: “We will continue to assist to the extent of our ability so long as this office remains in existence even though our staff has been reduced to become almost ineffective.”
And with that, the Case – by all available information – ended.
Verbatim transcripts of these four documents appear below.
________________________________________
Here’s Simon’s letter to the Army of March 4, 1946, written after he visited Edmund Farrell (295 Sterling Place) and Francis Kelly (403 Park Place), in Brooklyn.
COPY March 4, 1946
Dear Sirs:
Recently I visited the homes of T/Sgt Francis X Kelly and S/Sgt Edmund T. Farrell who were crew members on a Flying Fortress with my brother
) AGPC 201 Bartman Jack (
) MTO 176 Cpl. 32883370 (
who were shot down and their account which they say they gave repeatedly is in wide difference to all communications and versions we have received to date. As told to me the plane was hit at Bolzano and bailed out. Jack was fourth to bail out. He was captured at Lauregno by a civilian called Weiss and the Burgomaster who incited the people. A friendly civilian was the first to find my brother when he parachuted and he wanted him to go with him but Jack was distrustful and before he realized that he was friendly the others had found him. Jack gave this fella an airborne ring in token for his trying to be of help. The others led him up the road between Lana [sic] and Merano. They shot him in the head and buried him in an unmarked grave. The civilian that tried to befriend my brother later led the American authorities to the grave location. At that time I believe it was INS 9 or the 88th Division that did the investigating working with the British. The key pts. to investigate are at Merano & Bolzano. The people that know the story are located in town of Marcena de Rumo – Proveis – Lauregno.
He was killed the same day, April 20th. They all know the story for he was the only American killed there.
I hope this information will be of help.
Sincerely Yours,
Simon Bartman
COPY
________________________________________
This is the Docket Sheet filed on May 3, 1946, listing the names of the accused (Weiss, Gerlitsky / Gerlitzki, and Marzoner), Italian witnesses, and American witnesses, the latter members of Cpl. Bartman’s crew, plus Lt. Henry from the 450th Bomb Group.
Note the closing comments about the JA (Judge Advocate) of PES (?) and Trial Judge Advocate deeming evidence being insufficient for the case to stand trial, because “the claim was made that Cpl. Bartman was shot “while trying to escape.”
This is a statement – reads like something out of film noir, but it’s not fiction – that on occasion (I doubt if the total number has been quantified) can be found in Casualty Questionnaires within Missing Air Crew Reports pertaining to crews of 8th and 15th Air Force bombers. The statement typically appears in the context of comments, made either offhand or calculatedly by German interrogators or guards to surviving POWs of bomber crews, concerning fellow crewmen who – sometimes unwounded and uninjured when last seen, typically when bailing out – did not survive.
In the case of “Case 105”, was this statement a reason, or, a rationalization?
CASE 105
DOCKET SHEET
DATE: 3 May 1946
SOURCE: WD Report 16-293-5
DATE OF REPORT: 6 Sept. 1945
NATURE OF CRIME: Killing of wounded American Airman.
DATE OF CRIME: 22 April 1945
PLACE OF CRIME: near Lauregno, Italy (Lano to Merano)
NAME OF VICTIM(s): Corporal Jack BARTMAN, ASN 32883370
NAME(s) OF ACCUSED
Weiss, Giovanni (Johann)
GERLITZKI, Kurt 339 PW Camp
MARZONER, Gottfried 339 PW Camp
Major Heinemann (refusing honorable burial)
NAMES OF WITNESSES
GAISER, Giuseppe
HUBER, Francesco
ARINI, Adelino
BRUGGER, Alois (Luigi)
LUIGI PIRCHER PANCRAZI
SEGNA, Federico
Dr. Veith
American witnesses 483 Bomb Grp.
S/Sgt. Peter A. Filosena
S/Sgt. Ed Farrell
T/Sgt. William McDaniels
T/Sgt. Frank Kelly
2nd Lt. Robert G. Henry
S/Sgt. Lee Shead
STATUS OR DISPOSITION: JA of PES and Trial Judge Advocate consider evidence insufficient to warrant trial, the principal reason being that the claim is made that Bartman was shot while “trying to escape”. War Crimes Branch will attempt to convince the legal side that this claim was SOP in Northern Italy and will request a review of this case.
________________________________________
Here’s Colonel Barrett’s statement about the closure of the Case:
HEADQUARTERS
MEDITERRANEAN THEATER OF OPERATIONS
Office of the Theater Judge Advocate
UNITED STATES ARMY
APO 512
File No : JA 000.5/WCC # 1053 May 1947
SUBJECT : War Crimes Case #105.
TO : Civil Affairs Division
War Department Special Staff
Washington 25, D.C.
ATTN: War Crimes Branch
1. Reference War Crimes Case #105. War Department File: 16-293-5.
2. Subject War Crimes Case was administratively closed by this section and complete files forwarded to War Crimes Group, USFET for the reason indicated in attached copy of letter of transmittal.
TOM H. BARRETT
Colonel, JAGD
Theater Judge Advocate
THB/bp
Incls: a/s
________________________________________
Here’s Colonel Barrett’s letter of transmittal, detailing reasons for the Case’s closure. “We will continue to assist to the extent of our ability so long as this office remains in existence even though our staff has been reduced to become almost ineffective.”
File No : JA 000.5/WCC #105 3 May 1947
SUBJECT : Forwarding of War Crimes Case
TO : Deputy Theater Judge Advocate
7708 War Crimes Group, USFET
APO 178, U.S. Army
1. There is forwarded herewith the complete file of this office relative to a case which appears to have been a war crime committed by German personnel against a U.S. Prisoner of War. Investigation of the case over a long period of time indicates that most of the accused are either in Germany or in other areas under your jurisdiction and therefore the investigation cannot be completed in this theater.
2. In view of the imminent close-out of this theater and the necessity of terminating the War Crimes investigations on 1 May to permit the completion of cases now ready for trial, this case is forwarded to you for appropriate action in accordance with the War Department policy that you will assume the residual war crimes functions of this theater. It is believed that this will permit you to review these files and to request information deemed necessary from this area which might not otherwise be obtainable if transmission was not made until after close-out of the theater.
3. There are in custody in this theater the following named individuals:
Johann WEISS 110 5828
Kurt GERLITSKY 81 SP 199 350 H
Gottfried MARZONER 81 SP 766 01 Pol
Request you advise us at once of the disposition you desire made of the individuals in question, and also that you advise of any further information you may desire from here. We will continue to assist to the extent of our ability so long as this office remains in existence even though our staff has been reduced to become almost ineffective.
TOM H. BARRETT
Colonel, JAGD
Theater Judge Advocate
THB/bp
Incls: a/s
Cpy to WD Special Staff
________________________________________
Here’s Josef Laner’s article about the fate of 44-6861 and her crew, from der Vinschger, the cover of which appears below:

Als in Göflan der Bomber „landete”
When the Bomber “Landed” in Göflan
Das erste Foto nach der Notlandung des Bombers. Die herbeigeeilten Menschen wurden vom Südtiroler Ordnungsdienst (SOD) angehalten, auf Distanz zu bleiben, weil vermutet wurde, dass der Bomber explodieren könnte. Links ist der „Koflerhof” zu sehen, wo ein Flügel des Bombers den Dachfirst des Stadels gerammt hatte, rechts erkennt man die Dorfkirche zum Hl. Martin in Göflan.
The first photo after the bomber’s emergency landing. The people who rushed to the scene were asked by the South Tyrolean Public Order Service (SOD) to keep their distance because it was suspected that the bomber could explode. On the left you can see the “Koflerhof”, where a wing of the bomber rammed the roof of the barn, on the right you can see the village church of St. Martin in Göflan.

____________________
The article includes pictures of remnants of 44-6861, which (as of 2020, at least) had long been in the possession of residents of Göflan and Schlanders…
Luis Tumler aus Göflan mit einer Tankhalterung aus einem Flügel des Bombers. (links)
Herbert Tappeiner aus Schlanders mit einem Luft-Hydraulik-Zylinder. (mitte)
Gustav Angerer aus Schlanders (91 Jahre) war zur Zeit der Bruchlandung des Bombers Lehrbub beim Göflaner Schmied und in technischer Hinsicht der wichtigste Augenzeuge. (rechts) (Er steht neben einer Motorhalterung, wie im Diagramm unten aus der illustrierten Teileaufschlüsselung für die B-17G (USAAF Technical Order 1B-17G-4) dargestellt.)
Luis Tumler from Göflan with a tank mount made from a bomber wing. (left)
Herbert Tappeiner from Schlanders with an air-hydraulic cylinder. (center)
Gustav Angerer from Schlanders (91 years old) was an apprentice at the Göflan blacksmith at the time of the bomber’s crash landing and was the most important eyewitness from a technical point of view. (right) (He’s standing next to an engine mount, as depicted in the diagram below from the Illustrated Parts Breakdown for the B-17G (USAAF Technical Order 1B-17G-4).


____________________
And so, here’s the article…
Manfred Haringer ist seit 15 Jahren auf Spurensuche.
Zeitzeugen für Film gesucht.
GÖFLAN – Es war der 20. April des Jahres 1945, als in Göflan ein US-Bomber des Typs Boeing B-17G notlandete. Der 4-motorige Bomber hatte zusammen mit einer US-Bomberformation einen Einsatz im Gebiet von Franzensfeste und am Brenner geflogen, als einer seiner Tanks von der Kugel einer Flugabwehrkanone getroffen wurde. Gegen Mittag des genannten Tages befand sich der Bomber mit abgeschalteten Motoren im Gleitflug, als es beim „Koflerhof” in Göflan auf einem Acker zur Bruchlandung kam. Der Pilot und der Navigator wurden schwer verletzt und in das Krankenhaus nach Meran gebracht. Die weiteren 8 Crew-Mitglieder waren schon vorab mit Fallschirmen abgesprungen, die zwei letzten im Gemeindegebiet von Proveis am Nonsberg. „Der getroffene US-Bomber wollte die neutrale Schweiz erreichen”, ist Manfred Haringer aus Göflan überzeugt. Seit rund 15 Jahren befindet er sich auf der Spurensuche im Zusammenhang mit den Geschehnissen rund um die Bomber-Notlandung. Es ist mittlerweile eine dicke Mappe mit allerlei Dokumenten, Schriftstücken und Aussagen von Zeitzeugen zusammengekommen. Auch in Proveis und in Gemeinden des Nonstals im Trentino war Haringer unterwegs, um mit Menschen zu sprechen, die seinerzeit mit den abgesprungenen US-Soldaten zu tun hatten bzw. im Kontakt standen. Einer der abgesprungenen Soldaten, Jack Bartman, wurde von fanatischen Widerstandskämpfern erschossen. Sein Leichnam wurde nach Kriegsende in die USA überführt. Verwandte des Piloten Eugene T. Bissinger, dem es gelungen war, den Bomber in Göflan zusammen mit dem Navigator Nations Manton A. ohne Menschenverluste zu Boden zu bringen, waren im Vorjahr in Göflan. Der Aufbau von Kontakten zu Verwandten und Nachkommen der US-Crew-Mitglieder ist eines der Ziele, die Haringer verfolgt. Schon seit längerer Zeit gearbeitet wird außerdem an einem Film, der in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Amateurfilmer Verein Vinschgau entsteht und in dem vor allem Zeitzeugen zu Wort kommen, die die Bruchlandung direkt oder indirekt miterlebt bzw. beobachtet haben. Manfred Haringer ist weiterhin auf der Suche von Zeitzeugen. Solche können sich gerne bei ihm melden und zwar unter Tel. 339 5335534. Auch eine PowerPoint-Präsentation hat Haringer bereits zusammengestellt. Darin wird die gesamte Geschichte rund um die Landung nachgezeichnet, und zwar beginnend mit dem Bau der „fliegenden Festungen” in Seattle bis zur Bruchlandung in Göflan und der Zeit danach. In Göflan sorgte die Bruchlandung damals natürlich für großes Aufsehen. Alles lief zur Unglücksstelle. Viele nahmen später Teile des Bomber-Wracks mit nach Hause. Richard Reiter zum Beispiel, ein versierter Techniker, besorgte sich das Radiosendegerät aus dem Flugzeug. Für einige Monate konnten im Raum Schlanders seine Programme gehört werden, unter „Radio Stilfser Joch”, dem „Ersten Vinschgauer Radiosender”. Als Haringer die PowerPoint-Präsentation der Fraktionsverwaltung mit Präsident Erhard Alber an der Spitze zeigte, zeigte sich diese begeistert und froh darüber, dass die Geschichte rund um die Bomber-Notlandung umfassend und bleibend aufbereitet wird und somit der Nachwelt erhalten bleibt. Auch erste Vorbereitungen für eine Ausstellung sind bereits im Gang. Für diese Ausstellung zum Bomberabsturz wären Bomber-Relikte bzw. entwendete Teile davon sehr erwünscht und werden gerne entgegengenommen! An der Stelle, wo die Bruchlandung erfolgte, sollte eine Tafel angebracht werden. Manfred Haringer wertet seine Bemühungen und Recherchen im Zusammenhang mit dieser Geschichte in erster Linie als eine Art Friedensmission: „Das Wachhalten der Erinnerung an diesen Vorfall soll uns daran erinnern, wie schrecklich j e der Krieg und wie wertvoll der Frie de ist.” Detail am Rande: Für Flugzeuge und das Fliegen hat Manfred Haringer übrigens seit jeher einen „Fimmel”. Er war 1980 einer der ersten Drachenflieger im Vinschgau. Erlernt hatte er das Drachenfliegen von seinem um 4 Jahre älteren Bruder Hermann. Später widmete sich Manfred auch dem Bau von Flugzeug- und Hubschraubermodellen.
And, the English-language translation…
Manfred Haringer has been searching for clues for 15 years.
Contemporary witnesses wanted for film.
GÖFLAN – It was April 20, 1945, when a US Boeing B-17G bomber made an emergency landing in Göflan. The 4-engine bomber had been flying a mission in the area of Franzensfeste and Brenner along with a US bomber formation when one of its tanks was hit by a shot from an anti-aircraft gun. Around noon on the day mentioned, the bomber was gliding with the engines switched off when it crash-landed in a field near the “Koflerhof” in Göflan. The pilot and the navigator were seriously injured and taken to the hospital in Meran. The other 8 crew members had already jumped out with parachutes, the last two in the municipality of Proveis on Nonsberg. “The US bomber that was hit wanted to reach neutral Switzerland,” Manfred Haringer from Göflan is convinced. For around 15 years he has been searching for clues in connection with the events surrounding the bomber emergency landing. A thick folder has now been collected with all sorts of documents, papers and statements from contemporary witnesses. Haringer also traveled to Proveis and communities in the Non Valley in Trentino to talk to people who were involved or in contact with the US soldiers who had jumped ship. One of the soldiers who jumped [from the] ship, Jack Bartman, was shot by fanatical resistance fighters. His body was returned to the USA after the end of the war. Relatives of the pilot Eugene T. Bissinger, who managed to bring the bomber down in Göflan together with the navigator Manton A. Nations without any casualties, were in Göflan the previous year. Establishing contacts with relatives and descendants of the US crew members is one of Haringer’s goals. We have also been working on a film for some time now, which is being made in collaboration with the Vinschgau amateur filmmakers’ association and in which contemporary witnesses who directly or indirectly experienced the crash landing will have their say or have observed. Manfred Haringer is still looking for contemporary witnesses. They are welcome to contact him on Tel. 339 5335534. Haringer has also already put together a PowerPoint presentation. It traces the entire history of the landing, starting with the construction of the “Flying Fortress” in Seattle through the crash landing in Göflan and the period afterwards. Of course, the crash landing caused a great stir in Göflan at the time. Everyone ran to the scene of the accident. Many later took parts of the bomber wreckage home with them. Richard Reiter, for example, an experienced technician, got the radio transmitter from the plane. For a few months his programs could be heard in the Silandro area under “Radio Stilfser Joch”, the ” First Vinschgau Radio Station”. When Haringer showed the PowerPoint presentation to the parliamentary group administration with President Erhard Alber at the helm, they were enthusiastic and happy that the story surrounding the bomber emergency landing was being comprehensively and permanently prepared and thus preserved for posterity. Initial preparations for an exhibition are already underway. For this exhibition on the bomber crash, bomber relics or stolen parts of them would be very welcome and would be gladly accepted! A plaque should be placed at the spot where the crash landing occurred. Manfred Haringer sees his efforts and research in connection with this story primarily as a kind of peace mission: “Keeping the memory of this incident alive should remind us how terrible war is and how valuable peace is.” Detail on the side: By the way, Manfred Haringer has always had a passion for airplanes and flying. In 1980 he was one of the first hang gliders in Vinschgau. He learned hang gliding from his brother Hermann, who was four years older than him. Manfred later also devoted himself to building model airplanes and helicopters.
________________________________________
Some observations and thoughts…
First, it’s notable that of the three named accused in the Case File, Weiss went by the first name of both the Italian-sounding “Giovanni” or German-sounding “Johann”, while Gerlitsky / Gerlitzki and Marzoner also had German-sounding first names. Perhaps – just a thought? – this is no coincidence: a reflection of then demographic composition and political control of the South Tyrol during the Second World War. (Interestingly, the witnesses all had Italian first names.) As described in Wikipedia:
“South Tyrol as an administrative entity originated during the First World War. The Allies promised the area to Italy in the Treaty of London of 1915 as an incentive to enter the war on their side. Until 1918 it was part of the Austro-Hungarian princely County of Tyrol, but this almost completely German-speaking territory was occupied by Italy at the end of the war in November 1918 and was annexed to the Kingdom of Italy in 1919. The province as it exists today was created in 1926 after an administrative reorganization of the Kingdom of Italy, and was incorporated together with the province of Trento into the newly created region of Venezia Tridentina (“Trentine Venetia”).
With the rise of Italian Fascism, the new regime made efforts to bring forward the Italianization of South Tyrol. The German language was banished from public service, German teaching was officially forbidden, and German newspapers were censored (with the exception of the fascistic Alpenzeitung). The regime also favored immigration from other Italian regions.
The subsequent alliance between Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini declared that South Tyrol would not follow the destiny of Austria, which had been annexed to the Third Reich. Instead the dictators agreed that the German-speaking population be transferred to German-ruled territory or dispersed around Italy, but the outbreak of the Second World War prevented them from fully carrying out their intention. Every single citizen had the free choice to give up his German cultural identity and stay in fascist Italy, or to leave his homeland and move to Nazi Germany to retain this cultural identity. The result was that in these difficult times of fascism, the individual South Tyrolean families were divided and separated.
****
In 1943, when the Italian government signed an armistice with the Allies, the region was occupied by Germany, which reorganised it as the Operation Zone of the Alpine Foothills and put it under the administration of Gauleiter Franz Hofer. The region was de facto annexed to the German Reich (with the addition of the province of Belluno) until the end of the war. This status ended along with the Nazi regime, and Italian rule was restored in 1945.”
Second, though I cannot cite specific references, I’m under the general impression (?) that the investigation, prosecution, and punishment of war crimes in Italy – whether committed by the Wermacht, SS, or Italian Fascists; whether against Allied POWs, civilians, or Partisans – never had anywhere near the organizational support, focus, drive, and publicity that initially characterized the pursuit of justice for war crimes in the European (as opposed to Mediterranean) and Pacific theaters of war, even if this was eventually undermined and negated through a combination of apathy, Realpolitik of the (first) Cold-War, and economic interests. (For more on this disillusioning story read Tom Bower’s Blind Eye to Murder – Britain, America and the Purging of Nazi Germany – a Pledge Betrayed.)
Third, the dishonor shown to Cpl. Bartman’s body after his murder. The denial of an honorable burial, and especially, the refusal to allow any identifying information to be associated with Cpl. Bartman’s body and place of burial, was not only – necessarily – an attempt to conceal his murder. It was an attempt to obliterate his identity.
Fourth, I have no information about the subsequent fates of Johann / Giovanni Weiss, Kurt Gerlitsky / Gerlitzki, and Gottfried Marzoner, but it would seem that at least in terms of this case – 16-293-16 – nothing further followed. Perhaps – perhaps not? – they returned to the villages or towns where they resided. (If Weiss was a member of the “Landwacht” (Land Watch? Land Guard?), this would suggest that he was physically incapable of, and / or too old for active military service, and thus was performing some kind of auxiliary police duty. Perhaps in 1945 he was in his 40s, or, older.) Perhaps – perhaps not? – they lived the remainder of their lives and experienced the fullness of years. And, the world moved on.
____________________
Corporal Jack Bartman’s name is listed on page 270 of the 1947 book American Jews in World War II, where he is recorded as having been awarded the Purple Heart, Air Medal, and one Oak Leaf Cluster. His name also appears in Jacob L. Grimm’s Heroes of the 483rd. He completed 33 combat missions.
He was buried at Mount Hebron Cemetery in Flushing, New York in November of 1948.
This image of Jack Bartman’s matzeva is by FindAGrave contributor RJHorowitz…, who described himself in his profile with this inspirational statement: “Although a secular Jew, (I do not keep the Sabbath, kosher, light candles, attend services or give Zedakah as often as I should), I try to honor my ancestors, fellow Jews and my G-d one picture at a time.”
Jack Bartman’s Hebrew name, comprising the three words in the second line of text, is “Yaakov bar Moshe” (Yakov son of Moshe). Note that the stone incorporates symbols relating to both American and Jewish history. An eagle with thirteen stars. Below: to the left a Magen David, and to the right the winged star symbol of the Army Air Force.

This image of a dedicatory plaque at the base of the matzeva, also photographed by RJHorowitz, bears the text:
VIVIDLY ALIVE
IN THE HEARTS OF
YOUR PARENTS
BROTHERS AND SISTERS

This photo of the matzeva of Jack’s parents, Morris and Gussie, is by FindAGrave contributor MattFlyfisher. The Hebrew names of Jack’s parents were, respectively, Moshe bar Yitzhak (Moses son of Isaac), and Gilda bat Rav Avraham (Gilda daughter of Rabbi Avraham). Thus, Jack Bartman’s maternal grandfather was a rabbi.

____________________
And there the past remains.
It will always remain, even without the memory of man.
________________________________________
Note – Acknowledgement
Just as I was completing this post (!) I came across a discussion of the deaths of four POWs, at the 12 O’Clock High! forum. This eventually led me to information compiled by researcher Rolland Swank, comprising biographical profiles of the Bissinger crew, maps, a Mission Report, photographs, a description of the crash of 44-6861, images of some of the documents in the IDPF for Jack Bartman, and other documents. For example, it was within this material that I found the photos of Jack Bartman, his fellow crew members, the aerial photo Bissinger’s damaged B-17 (at the “top’ of the this post), and Arini Adelino’s translated letter of 1945.
So, I want to express my thanks and appreciation to Rolland for allowing me to use this information: “Thank you.”
References and Suggested Reading
Books
Birdsall, Steve, B-17 Flying Fortress in Color, Squadron/Signal Publications, Carrollton, Tx., 1986
Bower, Tom, Blind Eye to Murder – Britain, America and the Purging of Nazi Germany – A Pledge Betrayed, Granada Publishing Limited, Herts, England, 1981
Dublin, Louis I., and Kohs, Samuel C., American Jews in World War II – The Story of 550,000 Fighters for Freedom, The Dial Press, New York, N.Y., 1947
Grimm, Jacob L., Heroes of the 483rd: Crew Histories of a Much-Decorated B-17 Bomber Group During World War II, Georgia (?), 483rd Bombardment Group Association, 1997
Rust, Kenn C., Fifteenth Air Force Story, Historical Aviation Album, Temple City, Ca., 1976
United States National Archives (College Park, Maryland)
Records Group 92: Missing Air Crew Report 13817
Records Group 153: Case File 16-293-16
Websites
Axis War Crimes in Italy, at Wikipedia
atlante della stragi naziste e fascisti in italia (“Atlas of the Nazi and Fascist Massacres in Italy”), at http://www.straginazifasciste.it/
South Tyrol, at Wikipedia
South Tyrol, at Traces of Evil – Remaining Nazi Sites in Germany
May 26, 2021 – 463








































































































